Pregnancy-related deaths have become a pressing public health crisis in the United States, where the maternal mortality rate continues to rise, outpacing that of other high-income countries. Alarmingly, more than 80 percent of these deaths are preventable, underlining the urgent need for improved prenatal care and postpartum support. Recent studies reveal significant disparities in pregnancy-related deaths linked to factors such as race, ethnicity, and geographic location, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest risks. This concerning trend is compounded by an increase in chronic health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, among young mothers. To effectively address these health disparities and reduce maternal mortality rates, focused efforts on equitable healthcare access and targeted interventions are crucial.
The issue of maternal mortality, often described in terms like maternal health crises or pregnancy complications, highlights the growing concern around women’s health during and after pregnancy. Many women face significant risks during this vulnerable period, with recent data indicating alarming trends in pregnancy-related fatalities. Understanding the factors contributing to these preventable deaths is critical, especially given the broader context of health disparities that affect various racial and ethnic groups. Additionally, the rising prevalence of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease among pregnant individuals adds another layer of complexity to this urgent public health need. By fostering a more comprehensive approach to both prenatal and postpartum care, we can begin to address and mitigate the factors leading to these troubling statistics.
The Alarming Rise of Pregnancy-Related Deaths in the U.S.
Pregnancy-related deaths in the United States have seen a troubling increase, marking a significant public health concern. Recent studies indicate that the U.S. leads other high-income nations in maternal mortality rates, with more than 80% of these deaths classified as preventable. Between 2018 and 2022, pregnancy-related deaths surged, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2021. The unfortunate reality is that systemic flaws within the healthcare landscape, such as inadequate prenatal and postpartum care, contribute to these rising statistics, leaving vulnerable populations exposed to preventable risks.
As per new research, the data reflect stark variations across demographics, revealing that American Indian and Alaska Native women experience the highest mortality rates at an alarming 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births. This disparity highlights the urgent need for comprehensive reforms in maternal health policies. By addressing healthcare barriers and prioritizing equitable access to quality prenatal services, the U.S. can take crucial steps in reversing this distressing trend in pregnancy-related deaths.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
The primary causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are primarily cardiovascular disease, accounting for over 20% of such deaths, followed by hemorrhage and other complications. Understanding these causes is crucial for addressing maternal mortality.
How does the U.S. maternal mortality rate compare to other high-income countries?
The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with significant disparities based on race and state. More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, highlighting the need for better prenatal care and health equity.
What role does prenatal care play in preventing pregnancy-related deaths?
Prenatal care is essential in preventing pregnancy-related deaths as it allows for early detection and management of complications such as hypertension and cardiovascular diseases, which are leading causes of maternal mortality.
What disparities exist in maternal mortality rates among different racial and ethnic groups?
There are significant disparities in maternal mortality rates; for instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest rates, nearly four times that of white women. Addressing these health disparities is critical for reducing pregnancy-related deaths.
Why is postpartum care essential in the context of pregnancy-related deaths?
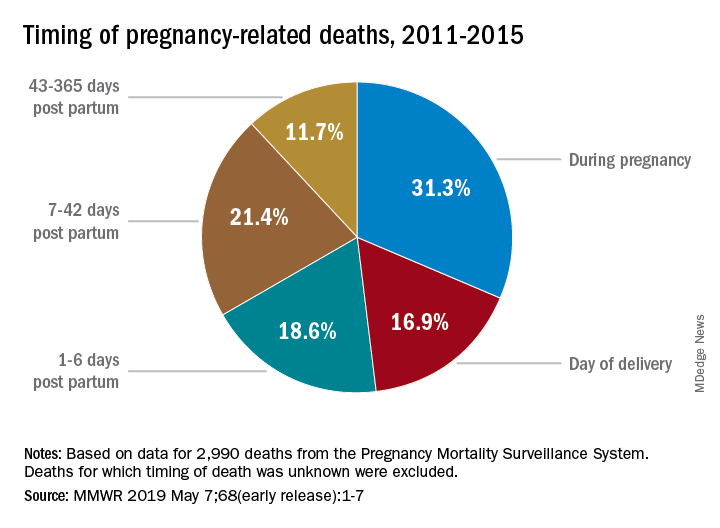
Postpartum care is vital as nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days and one year after delivery. Improved postpartum care can help identify and manage complications that arise during this crucial recovery period.
How has COVID-19 impacted pregnancy-related death rates in the U.S.?
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic likely contributed to a sharp increase in pregnancy-related death rates in 2021, exacerbating existing health disparities and complications, particularly among those with chronic health issues.
What actions can be taken to reduce pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
To reduce pregnancy-related deaths, investment in public health infrastructure and comprehensive pregnancy care is essential. Policies addressing disparities in access to healthcare, particularly prenatal and postpartum services, must also be prioritized.
How does cardiovascular disease specifically contribute to maternal mortality?
Cardiovascular disease, including conditions like hypertension and heart complications, has become the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, especially among younger women. Managing these chronic conditions before and during pregnancy is critical for maternal health.
What is the significance of tracking late maternal deaths in relation to pregnancy-related mortality?
Tracking late maternal deaths, or deaths occurring within one year postpartum, is significant as this period can involve serious health risks that contribute to maternal mortality. Including these deaths in mortality statistics emphasizes the need for extended healthcare support beyond 42 days postpartum.
What systemic issues contribute to the high rates of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
Systemic issues such as inequitable healthcare access, a fragmented healthcare system, and persistent biases within medical care contribute to high pregnancy-related death rates. Addressing these issues is essential for improving maternal health outcomes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Rates of Pregnancy-Related Deaths | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, continuing to rise from 25.3 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2018 to 32.6 in 2022. |
| Preventable Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, with many states showing considerable rate variations. |
| Impact of Racial Disparities | American Indian and Alaska Native women have the highest mortality rates (106.3 per 100,000), significantly higher than white women (27.6) and non-Hispanic Black women (76.9). |
| Leading Cause of Mortality | Cardiovascular disease, accounting for over 20% of deaths, has surpassed hemorrhage as the leading cause of pregnancy-related mortality. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Late maternal deaths account for nearly a third of total deaths, highlighting the need for extended postpartum care beyond the traditional 42-day marker. |
| Data Tracking Challenges | The inconsistency in national monitoring of maternal deaths until 2018 has hampered efforts to address the issue effectively. |
| Call for Action | Investing in public health infrastructure and addressing state-level policy differences is crucial for reducing pregnancy-related mortality rates. |
Summary
Pregnancy-related deaths have become a pressing issue in the U.S., as the country continues to have the highest maternal mortality rates among high-income nations. This alarming trend necessitates immediate action and investment in maternal healthcare. A significant number of these deaths are preventable, pointing to the need for enhanced prenatal and postpartum care to improve health outcomes. Addressing the disparities based on race, state policies, and ensuring adequate resources for all pregnant individuals is essential to turning this situation around. As calls for innovative solutions and better public health infrastructure grow, it is clear that a concerted effort is needed to combat the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths.