Alzheimer’s treatment has emerged as a critical focus in modern neuroscience, especially as new therapies evolve from innovative research. A recent breakthrough highlights the potential of TIM-3 therapy, an immune-system strategy initially developed for cancer treatment, to combat the devastating effects of Alzheimer’s. By targeting the TIM-3 checkpoint molecule, researchers found that they could free microglia—the brain’s immune cells—to effectively attack plaques in the brain that contribute to cognitive decline. This method not only enhances plaque clearance but also leads to improved memory functions in mouse models, marking a promising step forward for Alzheimer’s treatment. With ongoing studies, the future of Alzheimer’s therapy may redefine how we approach this debilitating disease, potentially ushering in new hope for millions.
As researchers delve deeper into the realm of cognitive impairment, the exploration of therapies aimed at Alzheimer’s disease unveils the intriguing potential of immune modulation strategies. Recent findings suggest that manipulating microglia, the brain’s resident immune cells, through checkpoint molecule management can reveal new avenues for addressing the accumulation of amyloid plaques. This innovative approach not only mirrors techniques used in cancer therapy but also paves the way for novel treatments tailored to enhance neuronal health. The concept of utilizing immunity to restore cognitive function is gaining traction, promising advancements in how we understand and treat Alzheimer’s and related neurodegenerative conditions. By rethinking traditional pathways, the quest for effective Alzheimer’s solutions is more dynamic than ever.
Overview of TIM-3 Therapy in Alzheimer’s Treatment
TIM-3 therapy represents a groundbreaking approach in Alzheimer’s treatment, focusing on the modulation of the immune response to combat the disease’s hallmark pathology. Recent studies suggest that inhibiting the TIM-3 checkpoint molecule can activate microglia, the brain’s resident immune cells, allowing them to effectively clear amyloid plaques from the brain. This innovative immune system strategy, initially developed for cancer treatment, highlights the potential of repurposing existing therapies for neurodegenerative diseases, providing a promising avenue for Alzheimer’s patients.
The implications of TIM-3 therapy extend beyond plaque clearance. By restoring the functionality of microglia, the therapy may also enhance cognitive function, leading to improved memory and overall brain health. Researchers have observed that genetic deletion of the TIM-3 molecule in mice resulted in significant cognitive recovery, marking a crucial advancement in our understanding of Alzheimer’s pathology. As we move forward, the challenge will be translating these findings into effective human treatments that can substantively alter the course of Alzheimer’s disease.
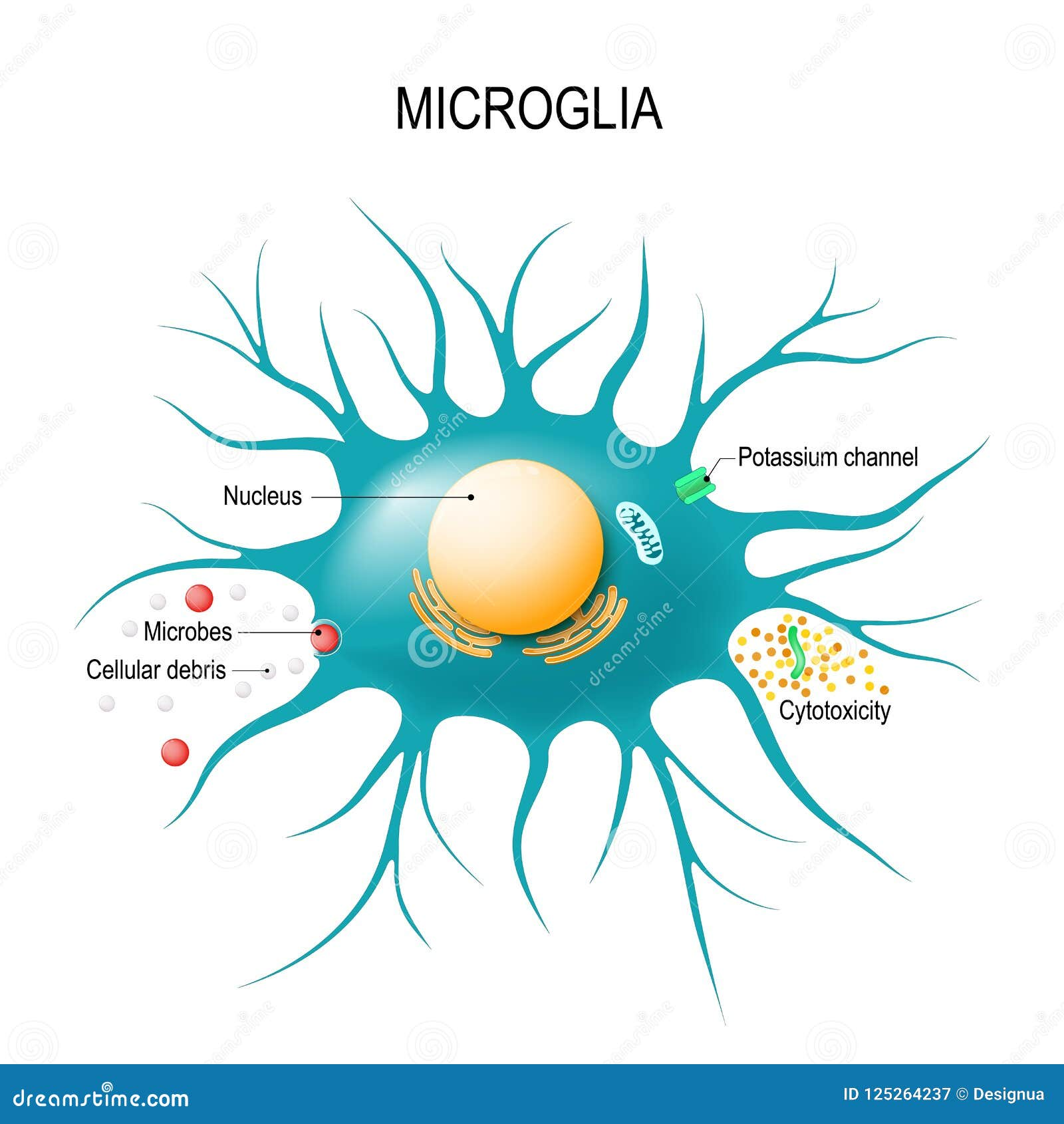
Understanding the Role of Microglia in Alzheimer’s Disease
Microglia play a fundamental role in maintaining brain health, acting as the primary immune defenders of the central nervous system. In Alzheimer’s disease, however, these cells become dysfunctional, primarily due to the overexpression of TIM-3, which inhibits their ability to phagocytose amyloid plaques. This dysfunctional state leads to plaque accumulation, contributing to neuroinflammation and subsequent cognitive decline. Identifying ways to enhance microglial function through TIM-3 modulation could not only facilitate plaque clearance but also restore the homeostatic balance within the brain.
As the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease progresses, microglia are faced with increased burdens, including the challenge of clearing protein aggregates like amyloid beta. The correlation between microglial inactivity and plaque buildup has raised critical questions about therapeutic strategies. By targeting TIM-3, researchers aim to reinvigorate microglial activity, potentially reversing some of the cognitive impairments associated with aging and Alzheimer’s. This interplay between microglia and amyloid pathology underscores the need for holistic approaches that address both immune dysregulation and neurodegeneration.
Cancer Treatment Strategies Applied to Alzheimer’s
The convergence of oncology and neurology has led to exciting prospects in Alzheimer’s treatment, particularly through the application of cancer therapies to neurodegenerative diseases. Checkpoint inhibitors, initially designed to boost the immune response against tumors, have prompted researchers to explore their effects on immune cells in the brain. The recent findings surrounding TIM-3’s role in both cancer and Alzheimer’s provide a compelling case for utilizing existing cancer therapies, potentially repurposing them for Alzheimer’s treatment.
Studies show that blocking TIM-3 enables microglia to engage more actively with plaque in the brain, leading to improved memory function in treated animal models. This approach not only presents a novel method for tackling Alzheimer’s but also emphasizes the need for interdisciplinary collaboration in research. The success seen in cancer treatment may illuminate paths for innovative therapies targeting Alzheimer’s, highlighting the potential benefits of leveraging immune system strategies across seemingly disparate medical fields.
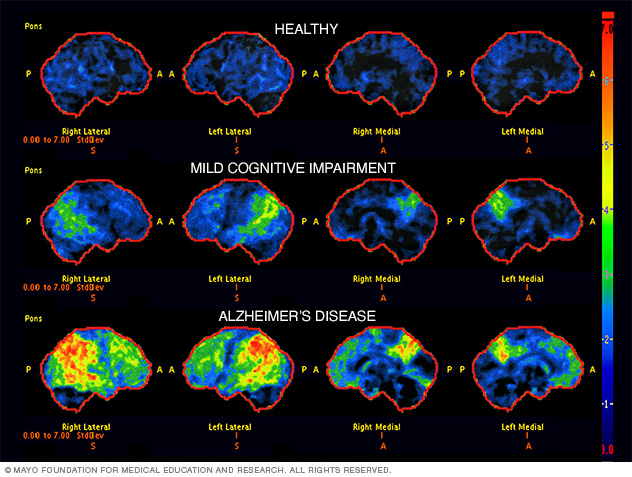
Impact of Amyloid Plaques on Cognitive Function
Amyloid plaques are a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease and are significantly associated with cognitive decline. These dense aggregates of amyloid-beta peptides interfere with neuron signaling and promote neuroinflammation, leading to cognitive deficits. Understanding the relationship between plaque accumulation and cognitive impairment is essential in developing effective therapies. The presence of plaques correlates with neurodegenerative processes that ultimately result in synaptic dysfunction and memory loss.
Research indicates that reducing amyloid plaque load enhances cognitive function, demonstrating the critical need for therapies focused on plaque clearance. Emerging treatments like TIM-3 therapy may provide the necessary tools to mitigate plaque buildup, restore microglial function, and improve memory. By targeting amyloid plaques, researchers hope to forge new paths toward effective Alzheimer’s treatments that can halt or reverse cognitive decline.
The Future of Alzheimer’s Research and TIM-3 Therapy
The future of Alzheimer’s research appears promising, particularly with the integration of TIM-3 therapy into treatment paradigms. Ongoing experiments with TIM-3 inhibitors are critical in determining their efficacy in human subjects, with early animal model results providing a strong foundation. The successful modulation of microglial activity in preclinical studies is paving the way for clinical trials aimed at establishing the real-world effectiveness of such therapies for Alzheimer’s patients.
Moreover, the exploration of TIM-3 therapy underlines a broader shift in neuroscientific research, where the immune system’s role in neurological diseases is receiving increasing attention. Future studies will likely explore the dose-response relationship, long-term effects, and safety profile of TIM-3 inhibitors. As the research progresses, the insights gained could not only reshape our understanding of Alzheimer’s but also enhance the therapeutic landscape for other neurodegenerative diseases.
The Mechanism of TIM-3 in Modulating Immune Response
TIM-3 functions as a negative regulator of the immune response, particularly in the central nervous system. By inhibiting the activity of T cells and microglia, TIM-3 prevents excessive inflammatory responses, an essential function during normal immune processes. However, this mechanism also leads to a failure of microglia to effectively clear toxic amyloid plaques, contributing to disease progression in Alzheimer’s. Understanding how TIM-3 modulates immune function provides insights into potential therapeutic interventions that could restore healthy immune responses.
By investigating the signaling pathways involved with TIM-3, researchers aim to uncover strategies that may enhance microglial function while controlling inflammation. This delicate balance is crucial, as excessive microglial activation can lead to collateral damage, further exacerbating neurodegeneration. Thus, unraveling the mechanisms by which TIM-3 operates could provide the key to developing targeted therapies that leverage the brain’s immune system to combat Alzheimer’s effectively.
Potential Risks and Considerations in TIM-3 Therapy
While TIM-3 therapy appears promising, it is essential to consider potential risks associated with immune modulation. Inhibiting TIM-3 could lead to unregulated immune responses, potentially increasing the risk of autoimmune reactions or neuroinflammation. Therefore, careful assessment of the therapeutic balance between enhancing microglial activity and avoiding excessive immune activation will be critical in the clinical applications of TIM-3 inhibitors for Alzheimer’s.
Additionally, understanding the long-term effects of TIM-3 inhibition is paramount. Since microglia have complex roles in neuroprotection and neurodegeneration, any treatment aimed at modulating their activity must be thoroughly evaluated for unintended consequences. Ongoing research will need to prioritize patient safety while exploring innovative approaches to harness TIM-3 therapy effectively.
The Importance of Collaborative Research in Alzheimer’s Solutions
Addressing the challenges of Alzheimer’s disease requires a collaborative approach among various disciplines within biomedical research. The integration of immunology, neurology, and therapeutic development is essential to uncover solutions that can effectively target the multifaceted nature of Alzheimer’s pathology. Researchers like Vijay Kuchroo emphasize that collaboration enhances the discovery process, as shared expertise can lead to more innovative and effective methodologies for disease treatment.
Collaboration also extends to partnerships with pharmaceutical companies and research institutions to ensure that promising findings can transition smoothly from laboratory settings to clinical applications. By fostering an environment of cooperation, researchers can leverage diverse perspectives and resources, ultimately accelerating the pace of Alzheimer’s research and therapy development. Such concerted efforts may lead to breakthroughs that significantly ameliorate cognitive decline associated with this devastating disease.
Enhancing Public Awareness and Understanding of Alzheimer’s Disease
Increasing public awareness of Alzheimer’s disease is vital in shaping attitudes toward research and treatment. Understanding the underlying mechanisms, such as the role of TIM-3 and the significance of immune response in Alzheimer’s pathology, can help demystify the disease and foster greater empathy for those affected. Educational campaigns can empower communities to engage with research initiatives and advocate for improved funding and resources for Alzheimer’s treatment and care.
Moreover, informed public discourse can facilitate meaningful conversations around Alzheimer’s, encouraging proactive approaches to health and wellness. With greater awareness, society can collectively prioritize the importance of scientific advancements, such as TIM-3 therapy, exploring their potential to change the landscape of Alzheimer’s treatment dramatically.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is TIM-3 therapy in relation to Alzheimer’s treatment?
TIM-3 therapy involves targeting the TIM-3 immune checkpoint molecule to enhance the activity of microglia, which clears amyloid plaques in the brain. Research indicates that inhibiting TIM-3 can help restore cognitive function and reduce plaque buildup associated with Alzheimer’s.
How does TIM-3 affect microglia and Alzheimer’s treatment?
TIM-3 serves as an inhibitory molecule that restricts microglial activity, preventing them from clearing harmful plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. By blocking TIM-3, researchers aim to boost microglial action against these plaques, potentially leading to better Alzheimer’s treatment outcomes.
Can cancer treatment strategies for TIM-3 be adapted for Alzheimer’s disease?
Yes, strategies successful in cancer treatment targeting TIM-3 can be adapted for Alzheimer’s treatment. By using anti-TIM-3 antibodies, researchers are exploring new therapies that may facilitate plaque clearance and improve cognitive functions in Alzheimer’s patients.
What role do microglia play in Alzheimer’s treatment?
Microglia are the brain’s immune cells responsible for clearing amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Enhancing their function through TIM-3 inhibition represents a promising approach in developing effective Alzheimer’s treatment strategies.
What’s the significance of plaques in the brain concerning Alzheimer’s treatment?
Plaques are aggregates of amyloid beta protein that accumulate in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients. Effective Alzheimer’s treatment aims to reduce plaque formation and promote its clearance by modulating immune responses, particularly through mechanisms like TIM-3 therapy.
How could TIM-3 therapy improve cognitive function in Alzheimer’s patients?
By inhibiting TIM-3, microglia become more active in clearing amyloid plaques, which is expected to improve cognitive function in Alzheimer’s patients. Studies show that when microglia can effectively reduce plaque burden, memory and overall brain health may improve.
What are the challenges with current Alzheimer’s treatment targeting amyloid plaques?
While targeting amyloid plaques has been a focus, many treatments face challenges due to poor delivery to the brain and potential side effects. TIM-3 therapy offers an alternative by enhancing the body’s immune response to manage plaque accumulation.
What future research is being done on TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s disease?
Future research on TIM-3 therapy includes testing humanized anti-TIM-3 antibodies in Alzheimer’s mouse models to assess their effectiveness in reducing plaque development and cognitive decline, potentially paving the way for new Alzheimer’s treatment options.
How long did the research on TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s take?
The research on TIM-3 therapy for Alzheimer’s took approximately five years, involving detailed studies on the role of TIM-3 in microglial activation and plaque clearance, showing promising results for future treatments.
What potential does TIM-3 therapy hold for Alzheimer’s disease patients?
TIM-3 therapy carries significant potential for Alzheimer’s disease patients by enhancing the brain’s innate immune response to clear plaque and possibly improving cognitive abilities, addressing a critical aspect of Alzheimer’s treatment.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Immune System Approach for Alzheimer’s | Research indicates that immune checkpoint strategies used in cancer treatment can be applied to Alzheimer’s disease, specifically through targeting the TIM-3 molecule. |
| Role of TIM-3 | TIM-3 is a checkpoint molecule that inhibits microglia, the brain’s immune cells, preventing them from attacking and clearing amyloid plaques associated with Alzheimer’s. |
| Study Findings | Deletion of the TIM-3 molecule improved cognitive function and plaque clearance in Alzheimer’s model mice. |
| Clinical Implications | Potential development of anti-TIM-3 therapies could offer new avenues for Alzheimer’s treatment by enhancing the brain’s immune response. |
| Research Funding and Collaboration | The study was carried out over five years, with partial funding from the National Institutes of Health and collaboration with specialists in the field. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s treatment is entering a new and hopeful phase with the promising findings regarding the TIM-3 immune checkpoint molecule. This research suggests a novel approach by leveraging immune system strategies, previously successful in cancer treatments, to target and clear the amyloid plaques that are characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease. With further studies and development, anti-TIM-3 therapies may provide significant cognitive benefits and pave the way for more effective treatments for patients suffering from Alzheimer’s.